Deploying a Node.js app to the Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)

Let us show you how quickly and easily you can deploy your app to Kubernetes on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
Create a new Kubernetes cluster
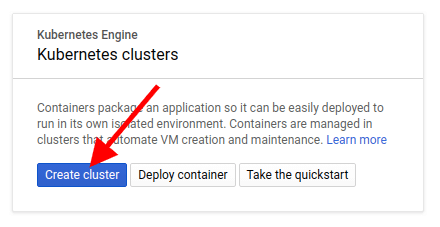
Enter a name for your cluster, the location, the number of nodes and the machine type. Then click More Options.
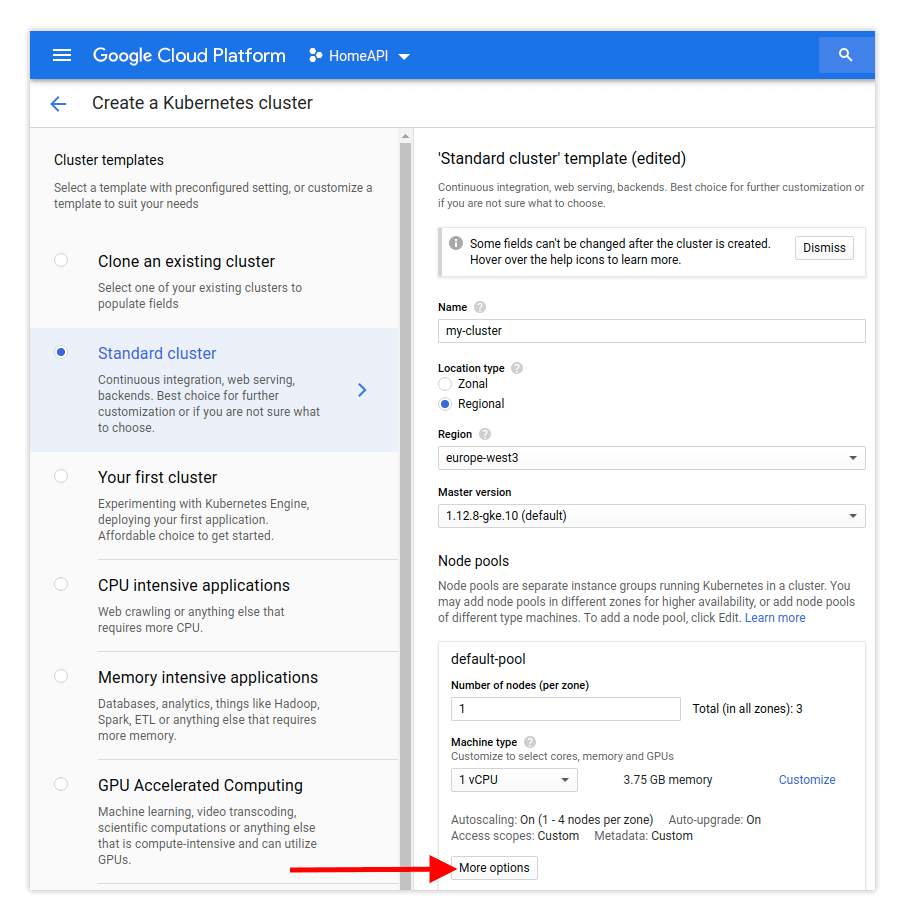
If you need to automatically add new nodes to the cluster, then click Enable autoscaling.

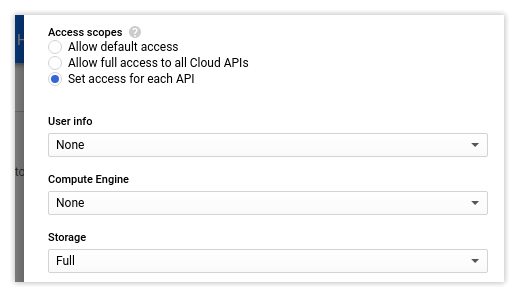
You can allow access to some APIs from the cluster. For example, I allow access to Google Cloud Storage (GCS).
After your cluster has been created, click Connect.
Now you’ll see a Cloud Shell containing the command; press Enter to execute it and get GKE credentials. After that, you can execute any commands with kubectl.
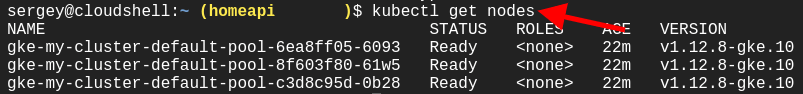
For example, let’s check the nodes of a cluster.
Push docker image to Google Container Registry
I’ll use my GitHub repo, which includes a simple Node.js app, Dockerfile, and deployment.yaml. I’ll enter all the following commands in Cloud Shell.
git clone https://github.com/sonufrienko/gke-simple-app cd gke-simple-app
Replace [PROJECT_ID] in deployment.yaml with your GCP project ID.
Get credentials to Google Container Registry
gcloud auth configure-docker
Build and push the docker image to Google Container Registry
docker build -t gcr.io/[PROJECT_ID]/app:v1 . docker push gcr.io/[PROJECT_ID]/app:v1
Deploy docker image to Kubernetes
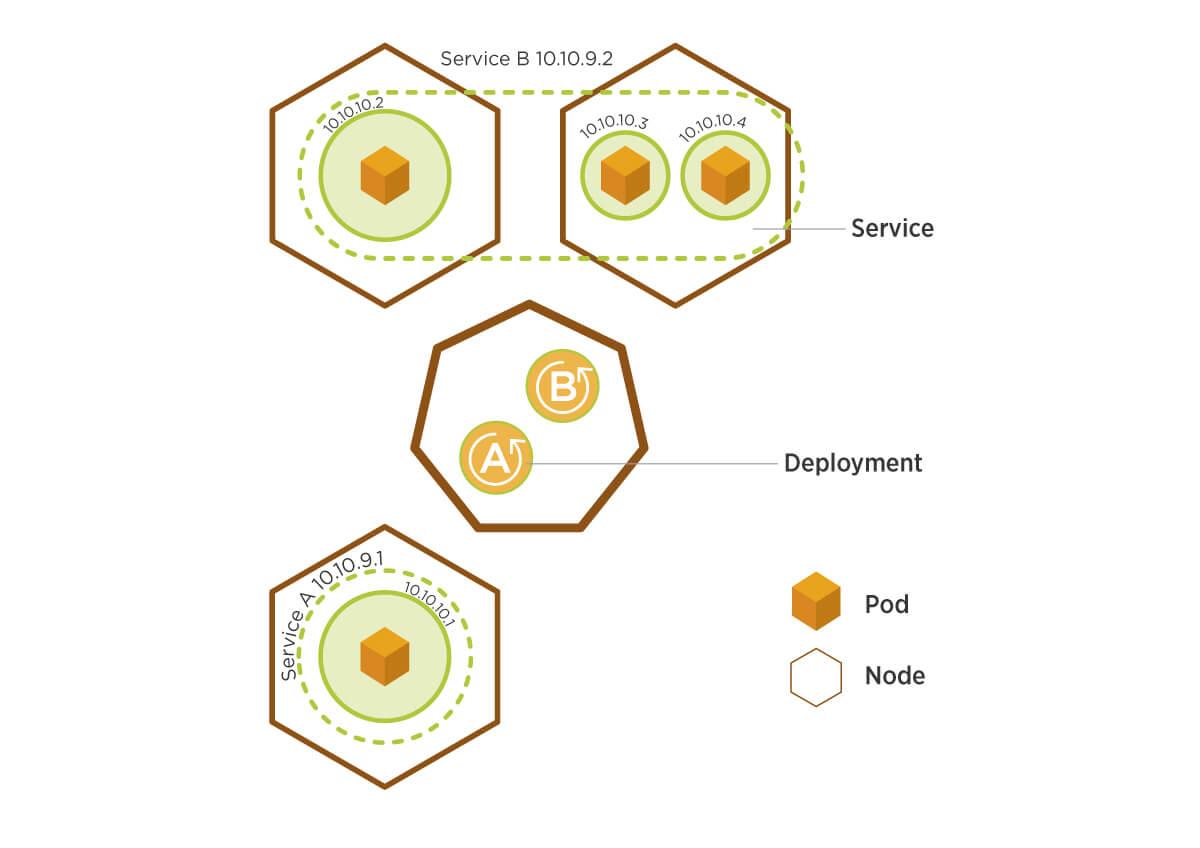
A deployment YAML file contains two parts:
- Deployment – describes the containers to be deployed
- Service – will create a LoadBalancer to expose our containers to the internet
Create deployment and service
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml --record
Check the deployment process
kubectl get deployments
Check the pods (containers)
kubectl get pods
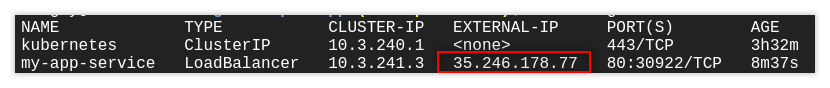
Check the service and copy the external IP address (LoadBalancer)
kubectl get services
Now, you can open this URL in your browser:
http://<EXTERNAL-IP>/encrypt?secret=abc&message=i-love-you
How to release a new version?
Push a new version of a docker image to the Container Registry, change the docker image version in deployment.yaml and then run this command to set desired deployment state:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml --record
How to rollback a new release?
kubectl rollout undo deployment/my-app-deployment
Useful tips
Check container logs
kubectl logs <POD NAME>
Go inside a container
kubectl exec -it <POD NAME> bash
Delete a whole deployment
kubectl delete deployment my-app-deployment
Set horizontal pod autoscaling policy for deployment
kubectl autoscale deployment <DEPLOYMENT_NAME> --max 6 --min 1 --cpu-percent 60
Check horizontal pod autoscaling policy (HorizontalPodAutoscaler object)
kubectl get hpa
Check pod Events to investigate issues with pod deployment, polling docker image, etc.