Narrowband (NB) IoT Standard: Definition, Benefits, How Does It Work?


The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing how we live and work, connecting billions of devices worldwide. According to Statista, over 75 billion devices will be connected to centralized networks and the world wide web by 2025. Today, we will explore what is narrowband IoT, a technology that offers enhanced connectivity, greater efficiency, and exceptional scalability for IoT applications. Join us in this NB-IoT guide as we uncover its inner workings, the features and advantages it brings, and how it stands up against other IoT communication protocols.
Narrowband IoT definition
NB-IoT, a low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) technology, has been specifically designed as a narrowband IoT standard to address the needs of IoT solutions requiring long-range communication and low bandwidth. Operating within the licensed spectrum, it has emerged in response to the unique communication challenges posed by the ever-growing number of IoT devices. Unlike smartphones, many IoT applications involve a multitude of devices that transmit small data packets infrequently, often located in remote or hard-to-reach areas where maintaining a stable connection is a priority.
Take, for instance, smart waste management systems in cities. With the help of NB-IoT-enabled sensors in waste bins, fill levels are reported to a central system, allowing for efficient route planning and waste collection schedule. This results in reduced fuel consumption, operational costs, and timely waste pickup. Or, in agriculture, farmers use NB-IoT-based soil moisture sensors to collect data on soil conditions, helping them make informed irrigation decisions and optimize water usage. Thanks to its long-range communication and low power consumption, a narrowband IoT network is a good choice for sensors in remote areas of large farms, minimizing the need for battery replacements.
How does the narrowband IoT work?
To truly grasp what is NB-IoT technology and its functioning, we should explore the technical elements that drive its operation. It is based on a set of standards and protocols designed to provide reliable, efficient communication for IoT devices with specific requirements.
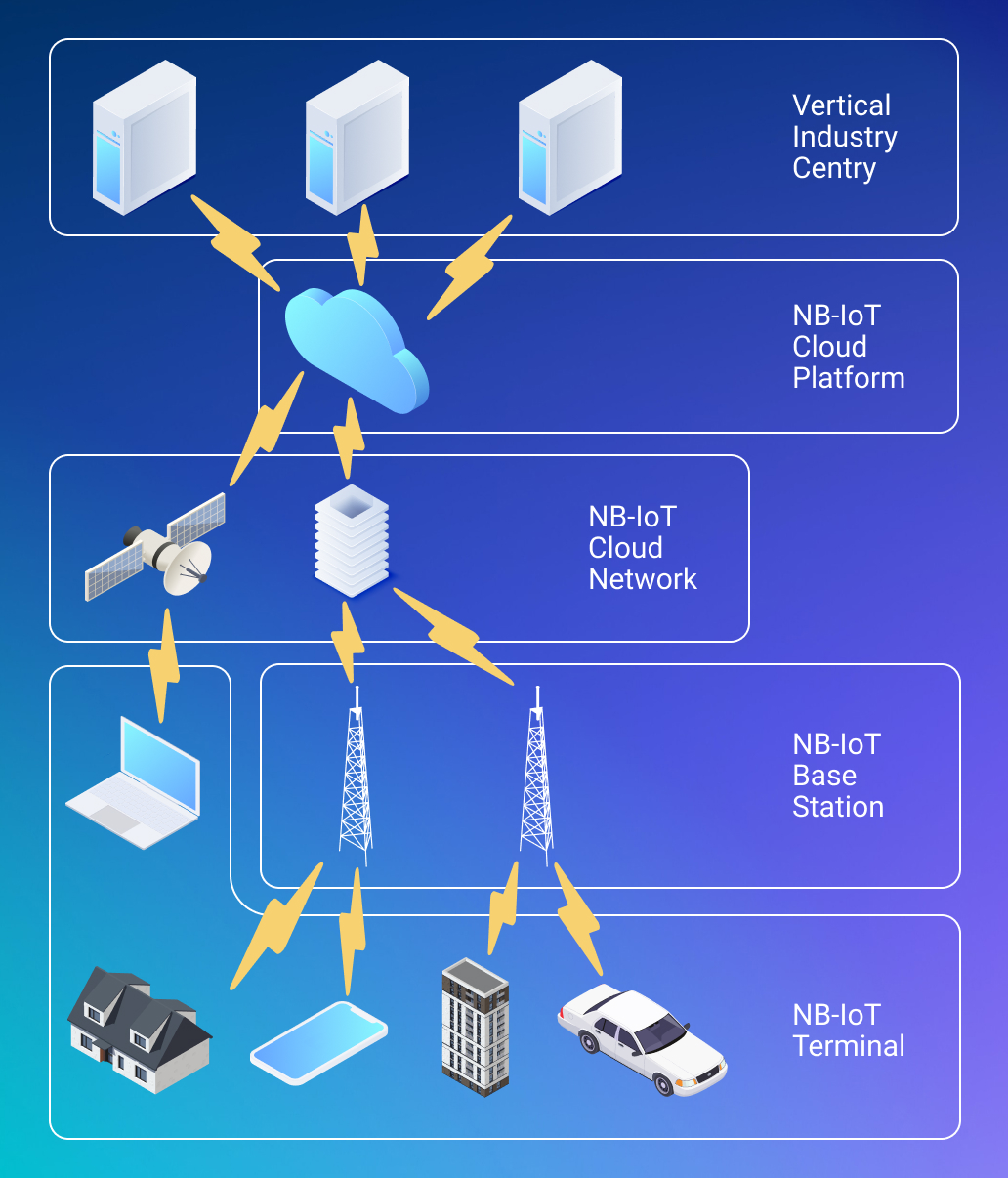
Radio access technology
At its core, NB-IoT employs a radio access technology that builds on existing cellular infrastructure, specifically leveraging the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) standards. Operating in a narrow frequency band of 200 kHz, it utilizes either in-band, guard-band, or standalone deployment options. This narrow frequency band ensures network efficiency and scalability, as it allows for accommodating a large number of devices within a limited spectrum.
Advanced modulation and encoding techniques
Employing cutting-edge techniques, this technology ensures reliable communication. SC-FDMA is used for uplink and OFDMA for downlink transmissions, providing enhanced spectral efficiency, reduced latency, and superior signal quality for extended coverage in challenging environments. Turbo Codes are utilized for error correction, maintaining data accuracy between devices and the network.
Effortless network infrastructure integration
The wireless architecture seamlessly integrates with existing cellular networks and capitalizes on mobile network operators’ infrastructure. It includes IoT devices, base stations, Mobile Core Networks, and IoT application servers. Protocols like RRC, PDCP, RLC, and MAC facilitate communication, managing device registration, connection setup, data transmission, and security.
Emphasis on energy efficiency
NB-IoT standard prioritizes low power consumption, featuring Power Saving Mode (PSM) and Extended Discontinuous Reception (eDRX). PSM allows devices to enter deep sleep states during inactivity, while eDRX enables intermittent wake-ups to check incoming data, synchronizing with the network at preset intervals, and maintaining connectivity.
Comprehensive security and data protection
Addressing security with measures like device authentication, data encryption, and integrity protection, this technology ensures a secure environment. Authentication uses pre-shared keys or certificates, ensuring only authorized devices access the network. Data encryption relies on SNOW 3G or AES algorithms, safeguarding data exchanges. Integrity protection verifies data remains unaltered during transmission.
What are the features of NB-IoT?
Being specifically engineered to address the distinct needs of IoT devices and applications, it has a variety of features that distinguish it from conventional cellular networks and other IoT communication technologies. In order to fully understand what is NB-IoT network, let’s take a look at the practical benefits each feature provides for businesses.
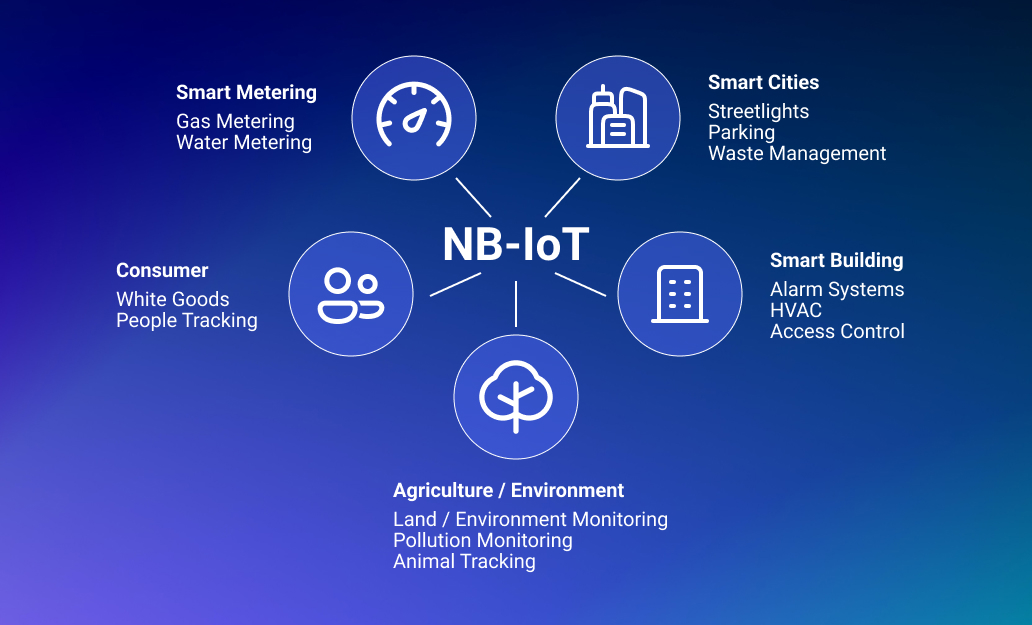
Expanding asset management reach
The enhanced coverage of this technology, achieved through sophisticated signal processing and leveraging cellular infrastructure, offers a considerable edge. With 20 dB more coverage than conventional networks, devices function in challenging environments like underground locations or deep inside buildings. This broad reach allows businesses to monitor and manage remote industry assets effectively, reducing operational costs.
Minimizing maintenance costs
Designed for low power consumption, IoT devices using this technology can operate for extended periods without constant battery replacement or recharging. Power-saving features help devices conserve energy when not actively communicating, which is vital for businesses deploying devices with long lifespans or in hard-to-reach locations. This significantly reduces maintenance costs and resource allocation.
Empowering scalable growth
As IoT devices proliferate, handling high device density becomes crucial. This technology supports up to 50,000 devices per cell, a much greater capacity than traditional networks. This elevated density allows businesses to scale their IoT deployments efficiently, enabling the smooth expansion of applications and fostering innovation.
Boosting ROI
This technology offers cost-effective connectivity for IoT devices with its narrow frequency band and streamlined radio access. Operating within a 200 kHz bandwidth simplifies radio hardware, lowering production costs. Furthermore, integration with existing cellular infrastructure minimizes deployment expenses. Affordable connectivity benefits cost-sensitive applications like smart metering and asset tracking, improving return on investment.
Safeguarding business data
Security is vital in IoT communications. This technology employs various features to protect devices and data, including authentication, encryption, and integrity protection. These measures ensure that only authorized devices access the network and that data remains secure and intact. By implementing robust security, businesses can protect sensitive information and reduce the risk of costly breaches.
Expedited market entry
Compatibility with existing cellular infrastructure, NB-IoT definition, streamlines deployment, and integration. Various configurations allow flexible integration with network resources, reducing deployment complexities and the need for additional infrastructure investments. By incorporating NB-IoT technology, businesses can adopt IoT solutions more rapidly, shortening the time to market and seizing IoT opportunities sooner.
NB-IoT vs. alternatives: Choosing the right IoT solution
In the realm of IoT connectivity, several competing technologies exist alongside Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT). Let’s compare prominent technologies to help you better understand what is NB-IoT standard, it’s differences, and choose the most suitable option for your IoT deployment.
NB-IoT vs. LTE-M
LTE-M, also known as Long-Term Evolution for Machines, represents an additional IoT communication protocol functioning in the licensed frequency bands. Although NB-IoT and LTE-M have some common traits, they address distinct IoT application requirements.
- Mobility: LTE-M supports device mobility, enabling seamless handovers between cells. This makes it well-suited for mobile IoT applications, such as vehicle tracking and wearable devices. In contrast, NB-IoT is better suited for stationary or low-mobility use cases, such as smart meters and environmental sensors.
- Energy efficiency: Both technologies prioritize energy efficiency, but NB-IoT focuses more on this aspect, providing longer battery life for devices that transmit small amounts of data infrequently. LTE-M, on the other hand, offers higher power consumption but compensates with increased data throughput and mobility support.
- Data throughput: LTE-M offers higher data rates than NB-IoT, with peak data rates of up to 1 Mbps. This makes it suitable for applications that require moderate data rates and low latency, such as real-time monitoring and control systems. In comparison, NB-IoT supports lower data rates, typically up to 250 kbps, making it more appropriate for applications with infrequent data transmissions.
- Network capacity: LTE-M can accommodate a lower number of devices per cell compared to NB-IoT. However, its support for adaptive data rate and better resource allocation makes it a suitable choice for IoT applications with variable data rate requirements.
NB-IoT vs. LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN (Low Range Wide Area Network) is a low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) technology that operates in the unlicensed spectrum. Like NB-IoT, it is designed for IoT applications requiring long-range communication and low bandwidth. However, there are notable differences between the two standards.
- Network control: As a licensed spectrum technology, NB-IoT offers a more controlled and predictable network environment, with reduced interference and more robust quality of service. LoRaWAN, being unlicensed, is more susceptible to interference, which may affect its reliability and performance.
- Range: Both technologies provide long-range communication, but NB-IoT typically offers better indoor penetration due to its use of existing cellular infrastructure. LoRaWAN, on the other hand, may have a longer range in certain outdoor scenarios.
- Deployment costs: NB-IoT leverages existing cellular infrastructure, which can lead to lower deployment costs for network operators. LoRaWAN requires the deployment of dedicated gateways, which can incur higher upfront costs.
- Scalability: While NB-IoT supports a high device density, LoRaWAN’s network capacity can be more easily scaled by deploying additional gateways. This flexibility in scalability allows for a more customized approach to network expansion, catering to the specific needs of the IoT application.
NB-IoT, LTE-M, LoRaWAN: A Concise Comparison
Looking to compare NB-IoT, LTE-M, and LoRaWAN? Check out this comparison table, where we’ve highlighted some key features, making it easier for you to choose the perfect IoT connectivity option tailored to your needs.
| Characteristic | NB-IoT | LTE-M | LoRaWAN |
| Spectrum | Licensed | Licensed | Unlicensed |
| Frequency Bands | 700 MHz – 2.6 GHz | 700 MHz – 2.6 GHz | 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz |
| Bandwidth | 200 kHz | 1.4 MHz | 125 kHz, 250 kHz, 500 kHz |
| Data Rate | Up to 250 kbps | Up to 1 Mbps | 0.3 kbps – 50 kbps |
| Range | 10-15 km (rural), 1-2 km (urban) | 7-10 km (rural), 1-2 km (urban) | 2-5 km (urban), 15 km (rural) |
| Device Density | Up to 50,000 devices per cell | Up to 1,000 devices per cell | Varies based on gateway density |
| Mobility Support | Limited | High (seamless handover) | Limited |
| Latency | <10 seconds | <100 ms | Varies (seconds to minutes) |
| Deployment Costs | Lower (utilizes existing infrastructure) | Lower (utilizes existing infrastructure) | Higher (requires dedicated gateways) |
| Geolocation | Cell-ID based | Cell-ID, OTDOA, GPS | TDoA, RSSI based |
| Indoor Penetration | High | Moderate to High | Moderate |
Note: that actual specification values may vary depending on the implementation, environment, and network configuration.
Conclusion
When it comes to the IoT landscape, it’s really important to find the right connectivity solution. Today, we traveled through a narrowband IoT guide and looked at three contenders in this race: NB-IoT, LTE-M, and LoRaWAN, each with its own set of advantages. NB-IoT is all about broad coverage and energy efficiency, making it a great choice for stationary or low-mobility applications. On the other hand, LTE-M supports mobility and handling higher data throughput, which is perfect for devices on the move. And let’s not forget about LoRaWAN, which offers excellent long-range communication in the unlicensed spectrum. To make the best decision, carefully assess your business requirements and goals. Take factors like coverage needs, device mobility, and power consumption into account. By doing so, you can ensure successful IoT deployments and unlock the true potential of your applications.
Sirin Software: Your Go-To Expert for IoT connectivity solutions
Navigating the complex world of IoT connectivity can be a daunting task, but Sirin Software is here to help as your trusted partner. Our staff provides specialized solutions to match your unique demands thanks to our significant experience and knowledge. We’ve worked on projects like managing wireless connections for consumer electronics (Learn more) and improving connection standards for smartwatches (Learn more), showcasing our ability to handle complex IoT challenges. Specializing in various IoT applications, including NB-IoT, LTE-M, and LoRaWAN, we offer end-to-end support, from consulting and strategy development to implementation and maintenance. You can be sure that your projects will be carried out precisely and expertly by working with us. Whether you want to benefit from our expertise or need a more comprehensive explanation of IoT connectivity, don’t hesitate to reach out to Sirin Software.
FAQ
Is NB-IoT 5G?
NB-IoT is not exactly 5G, but it is an integral part of the 5G ecosystem and plays a significant role in supporting IoT use cases within the broader 5G framework. While initially developed as a 4G technology, NB-IoT has evolved to complement and enhance 5G connectivity, particularly for low-power, wide-area IoT applications.
What is the difference between LTE and NB-IoT?
The main differences between the two lie in their focus on data transfer rates, coverage, power consumption, and use cases. NB-IoT is ideal for IoT applications involving a large number of devices transmitting small amounts of data infrequently.
How does NB-IoT impact businesses?
NB-IoT offers several advantages to businesses, including extended coverage, low power consumption, and simple deployment. By adopting NB-IoT technology, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation in various industries, such as smart metering, asset tracking, remote monitoring, smart agriculture, and smart city infrastructure.