The Industrial Internet and wireless systems have enormous potential to improve the control and monitoring of various processes and equipment in distributed automation systems. A total wireless significantly reduces costs (up to 30% in simple configurations), especially for large-scale installations in distant locations.
Where wiring is expensive or impossible, wireless connectivity allows the most efficient appliances to be connected. However, the harsh production conditions make it difficult to achieve the required productivity. With an increasing number of deployments, enterprises need help selecting solutions based on operational requirements. In this article, Sirin Software presents its own approach to enterprise wireless solutions.
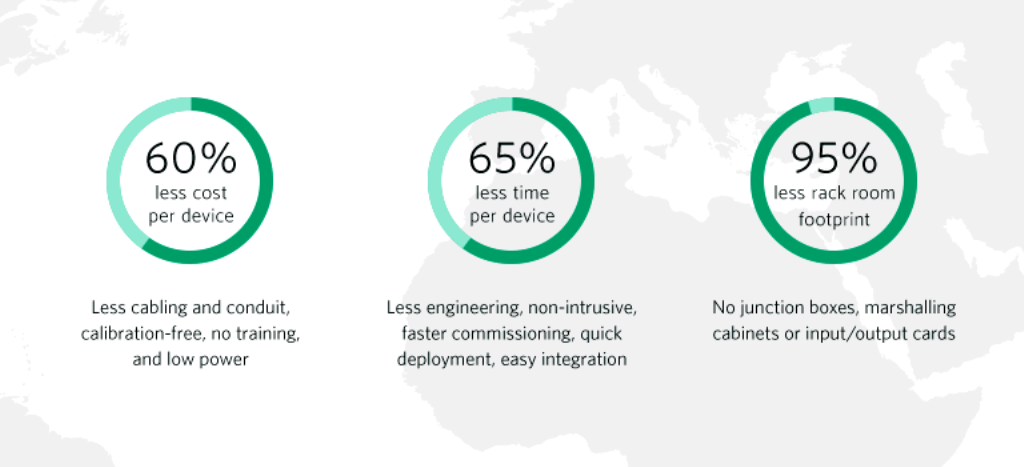
Enterprise Wireless Solutions Advantages
The ultimate advantages of an implemented wireless system include:
- Lower cost, especially when installing a large number of devices.
- Controllability. Wired solutions are reliable, but as opposed to wireless systems, they are not capable of reporting failures. Through preventive measures and diagnostics, wireless failures can be minimized.
- Flexibility. After the full implementation of a wireless system, new sensors can be easily added for more data to be transferred.
- Safety. Security depends on the device and not on the physical capabilities of the transmission equipment.
- Reservation. The wired tester is connected with a single wire. The redundant wireless link can be absolutely reliable when the wires are long or in difficult conditions.
- Enterprise-level redundancy. Total wireless can add redundancy by transmitting the same data over both wired and wireless links.
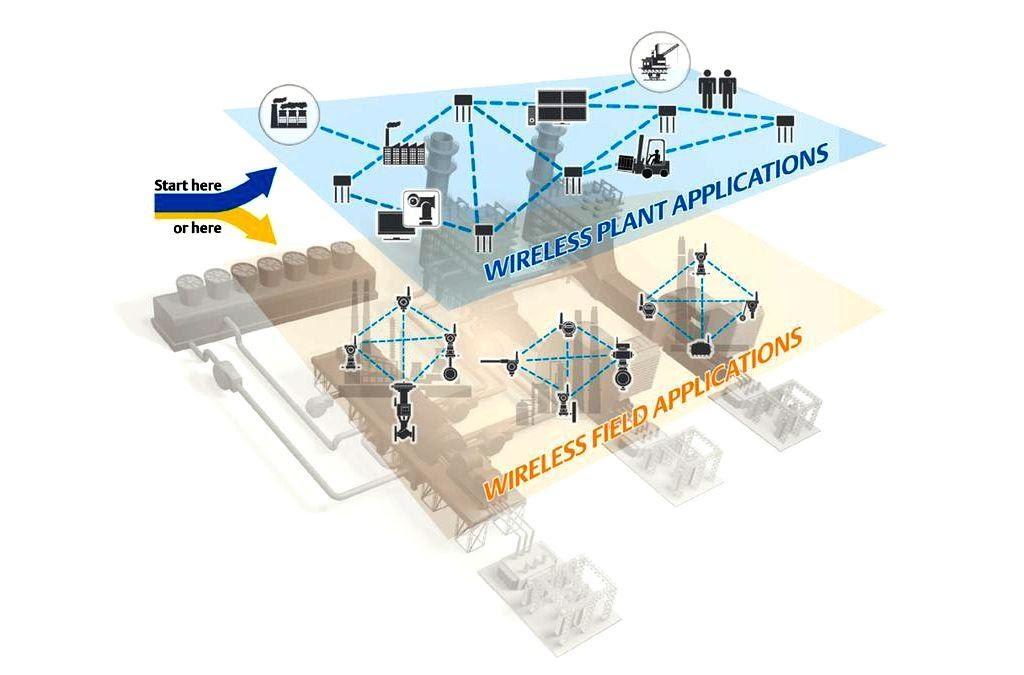
Major Issues with a Wireless System and Ways to Solve Them
Currently, we can point out four major issues related to the total wireless.
High reflectivity of signals
For signals at typical 900 MHz and 2.4 GHz radio frequencies, concrete, metal, any large obstruction creates an environment in which noise, echo and interference are unavoidable. Electromagnetic radiation from manufacturing equipment affects the power and transmission flow of signals. The introduction of an enterprise wireless solution is hindered by the sharing of the same frequency channels.
Solutions to this aspect include:
- FHSS (Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum) – a method of data transmission with a change in carrier frequency. The frequency changes in accordance with a pseudo-random sequence of numbers, therefore, the noise immunity of the communication channel increases many times.
- DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) is a method of transmitting information simultaneously over all available channels (or with a change in frequency within a set of orthogonal carriers), which makes it faster in signal-congested environments, but requires a wider bandwidth.
No support for manufacture protocols
Wireless technologies were originally designed for the general consumer, but were intended for home and corporate use. Therefore, very few hardware designers used industrial protocols such as Modbus, RS-232, 422, or 485.
New industry standards are now being created to increase the reliability, safety, speed, range, and efficiency of wireless mobi solutions:
- Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11 b/g/n, 802.11ac и 802.11ax);
- Bluetooth (IEEE 802.15.1);
- ZigBee (IEEE 802.15.4);
- Proprietary RF (non-standard).
Length and speed of work
The pioneer wireless mobi solutions did not have long range. Sensors and receiving equipment had to be placed in close proximity. Thanks to Wi-Fi 6 and a frequency of 5 GHz, today, their signal can be spread over tens of meters without any problems. The problem is solved with:
- more powerful sensors with increased sensitivity;
- line of sight (LOS) omnidirectional antennas;
- boosted reception capacities.
The modern 802.11ac standard provides data transfer rates up to 6.9 Gbps in the 5 GHz band. That’s 10x faster than 802.11n. And support for MU-MIMO technology allows simultaneous monitoring of multiple devices.
Wave 2 products show performance up to 2.34 Gbps. Next-generation APs are compatible with Wave 1, 802.11n and client devices. But the capabilities of the 2nd generation adapter cannot be used with the point of the first.
Security
The introduction of IEEE 802.11 standards has raised a lot of security issues for enterprise wireless solutions. The latest industry security standards IEEE 802.11i/WPA2 address these issues.
- Firewall protection devices are used to verify the authenticity of the messages received.
- Intra-network filtering of routed and internetwork traffic is provided by wireless intrusion detection systems.
- Wireless systems enable a more thorough detection and reporting of an extensive range of suspicious actions.
Summary
To meet the demanding and conflicting requirements for future wireless mobi solutions, many technical challenges need to be addressed, such as:
Technological breakthroughs are expected in wireless communications for the foreseeable future. Sirin Software adopts the best practices of the latest technology trends to meet the needs of customers in a variety of industries. Our total wireless solutions are designed to meet the modern individual requirements of projects of any complexity.