Zigbee vs. Z-Wave: Comparison, Pros & Cons, How Do They Work?

While Z-Wave and Zigbee share some similarities as wireless communication protocols, there are notable differences that can make one more appropriate than the other for specific applications. To help you navigate these distinctions, this article will provide a thorough comparison of Z-Wave vs. Zigbee. We’ll examine each protocol’s distinct features, advantages, and drawbacks, as well as their working principles. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced user of smart automation technology, this article offers valuable insights and guidance to help you choose the optimal wireless communication protocol for your specific needs.
How Does Zigbee Work?
Zigbee is a wireless communication protocol built on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. Operating in the 2.4 GHz frequency band globally and 915 MHz in the US, Zigbee offers a communication range of approximately 10-100 meters (33-328 feet), depending on environmental factors. It excels in providing mesh networking capabilities, supporting over 65,000 nodes in a network. This scalability makes it ideal for extended deployments in applications like industrial automation and smart city projects.

The Zigbee communication stack consists of several layers, including the Application Support Sublayer (APS) and Zigbee Device Objects (ZDO), which manage device-specific functions and enable devices to join or leave a network. Zigbee networks provide flexibility in network routing through the use of multiple routing algorithms like Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) and tree routing. This adaptability allows the network to optimize communication paths and performance based on specific use cases or environmental conditions. The Zigbee Alliance supports the development and standardization of the protocol, fostering a diverse ecosystem of devices from various manufacturers.
Pros And Cons of Zigbee
In the realm of smart automation technologies, Zigbee stands out as a popular wireless communication protocol. By analyzing its benefits and drawbacks, we’ll assist you in deciding if it suits your specific demands.
Pros
1) Open standard and flexibility:
Zigbee is an open standard, which encourages innovation and competition among manufacturers. This results in a wide variety of devices and applications, enabling the creation of custom solutions for different needs.
2) High scalability and large networks:
Zigbee networks can support up to 65,000 devices, making them suitable for large-scale installations in industrial, commercial, and residential settings. The mesh networking capability allows for increased network resilience.
3) Multi-hop communication:
Zigbee’s mesh topology supports multi-hop communication, allowing devices to transmit messages via up to 30 intermediate nodes. This extends the network’s range without extra infrastructure and enhances fault tolerance by rerouting messages around obstacles or failed nodes, ensuring critical data reaches its destination.
Cons
1) Interference and network congestion:
Zigbee operates in the 915MHz in the US, but also at the 2.4 GHz frequency band globally, which is also used by Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other wireless technologies. This can result in interference and network congestion, potentially affecting the performance and reliability of Zigbee devices.
2) Complexity and compatibility:
Being an open standard, Zigbee’s multiple profiles and device types can lead to compatibility issues between devices from different manufacturers. Moreover, setting up and configuring Zigbee networks may be more complex for some users.
3) Fragmented application profiles:
Zigbee’s application profiles, designed to address various use cases, can sometimes result in a fragmented ecosystem. Developers may face challenges in integrating devices that adhere to different profiles, leading to increased development time and complexity when creating cross-functional solutions.
How Does Z-Wave Work?
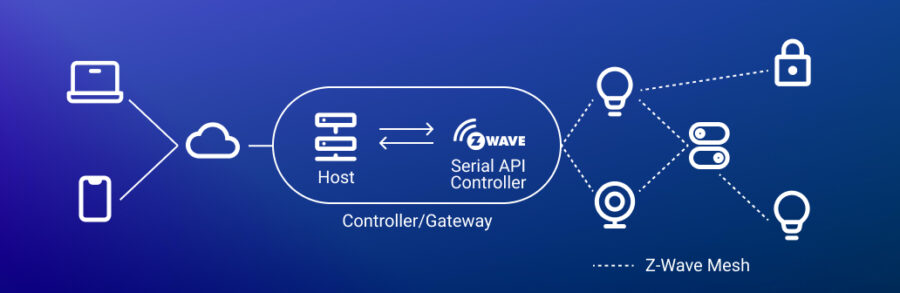
Z-Wave is a wireless communication protocol based on the ITU-T G.9959 standard. Operating in the sub-1 GHz frequency band, Z-Wave provides a decent communication range, between 30-100 meters (100-330 feet), depending on the environment. It supports mesh networking with up to 232 nodes, utilizing the Source Routing Algorithm (SRA) for dynamic route optimization. This capability makes Z-Wave well-suited for residential and small-scale commercial applications.
Z-Wave’s certification process, known as “Z-Wave Plus,” emphasizes interoperability and user experience. This ensures seamless compatibility among devices and enhances the user experience in home automation applications. The Z-Wave ecosystem is specifically tailored for residential projects, such as smart lighting, security systems, and climate control, offering a cohesive user experience for various home automation solutions.
Pros And Cons of Z-Wave
Z-Wave, positioned as a leading smart home wireless protocol, also has its pros and cons. We will highlight the most important aspects, enabling you to evaluate whether Z-Wave is better than Zigbee for your specific requirements.
Pros
1) Reliability and reduced interference:
Z-Wave operates in the sub-GHz frequency band, reducing the likelihood of interference with other common wireless technologies like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, which operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. This contributes to greater network reliability and performance.
2) Interoperability:
Z-Wave devices from different manufacturers are highly compatible with one another, allowing for seamless integration and flexibility in system design.
3) User-friendly setup and installation:
Z-Wave devices are generally easy to set up and install, making them suitable for consumers and DIY enthusiasts.
Cons
1) Limited device capacity:
Z-Wave networks can support up to 232 devices, which might not be sufficient for extensive industrial or commercial installations, limiting its scalability compared to Zigbee.
2) Regional frequency differences:
Z-Wave operates on different frequency bands depending on the region, which can cause incompatibilities when using devices from different countries, potentially complicating international use and support.
3) Limited data rates:
Z-Wave, primarily designed for smart home automation, has a limited data rate of 9.6 kbps to 100 kbps, which can slow down device communication and affect response times as well as real-time data processing. This constraint may cause congestion and latency in extensive networks, impacting overall performance. As the technology progresses, Z-Wave’s limitations could impede adaptation to new requirements, potentially requiring alternative protocols or infrastructure upgrades.
Difference Between Zigbee and Z-Wave

While both topologies are based on mesh networking principles, there are several key differences between the two, stemming from differences in their protocols, network management, and device capabilities. Here’s a more detailed Z-Wave versus Zigbee comparison:
- Data transfer rate:
Z-Wave’s data rate ranges from 9.6 to 100 kbps, while Zigbee’s reaches up to 250 kbps. This disparity can impact performance in high-throughput or real-time communication applications.
- Data transfer range:
Zigbee vs. Z-Wave range varies, with Z-Wave devices typically having a range of 30-100m (100-330ft) and Zigbee devices ranging from 10-100m (33-328ft), showing a lower minimum range for Zigbee. But keep in mind that environmental factors, device power, and antenna design affect both standards’ ranges.
- Power consumption:
Both Z-Wave and Zigbee are designed to be low-power protocols, making them suitable for battery-operated devices. However, Z-Wave vs. Zigbee difference in this aspect plays in favor of the second, because Zigbee generally has a slight edge in terms of power efficiency due to its lower power consumption.
- Compatibility:
Z-Wave devices undergo rigorous certification, guaranteeing compatibility across manufacturers. Zigbee has certification too, but compatibility can be more difficult due to multiple Zigbee profiles.
- Security:
Both Z-Wave and Zigbee have robust security. Z-Wave employs AES-128 encryption and the S2 framework for enhanced security, while Zigbee uses AES-128 encryption, secure key establishment, and application-level security.
- Complexity:
Setting up and managing a Z-Wave network is generally user-friendly, making it suitable for DIY enthusiasts. Zigbee networks can be more complex due to the larger variety of devices, profiles, and potential compatibility issues.
- Scalability and Device Limitations:
Supporting up to 65,000 devices, Zigbee is suitable for large-scale and complex networks. With a 232-device limit, Z-Wave suffices for home automation and small to medium-sized IoT applications but may not suit larger networks.
- Cost:
Z-Wave devices are often pricier than Zigbee counterparts, partly because Z-Wave is proprietary while Zigbee is an open standard. The cost disparity may also stem from a wider variety of Zigbee device manufacturers.
In summary, to answer the question “how to choose between Z-Wave and Zigbee”, Consider aspects like cost, data rate, range, power usage, compatibility, security, complexity, and scalability to select the best wireless protocol.
Comparison Table: Zigbee versus Z-Wave
| Feature | Zigbee | Z-Wave |
|---|---|---|
|
Frequency Band |
915MHz (US)
2.4 GHz (worldwide) |
908.42 MHz (US) 868.42 MHz (Europe) |
| Data Rate | 20-250 kbps | 9.6-100 kbps |
| Connection Range | 10-100 meters (33-328 feet) | 30-100 meters (100-330 feet) |
| Routing length | 30 hops | 4 hops |
| Power Consumption | Slightly lower | Slightly higher |
| Price | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Complexity | Slightly more complex | Slightly less complex |
| Protocol Standard | IEEE 802.15.4 (Zigbee) | ITU-T G.9959 (Z-Wave) |
| Max. devices per network | 65,000 | 232 |
| Security Features | AES-128 encryption | AES-128 encryption |
| Main Advantages | Higher data rate, lower cost, wider device support | Longer direct connection range, easier setup, less interference |
What Technology is Better for Your Project?
Selecting the right wireless protocol for your project can be complex. We’ll try to help you to choose between Z-Wave and Zigbee, enlightening key factors to ensure you make an informed decision.


How Sirin Software Can Help?
Sirin Software, a leading tech solutions provider, excels in delivering innovative, high-quality services for a wide range of applications. Our strength lies in our deep understanding of diverse technologies, our focus on customer satisfaction, and our ability to create custom industry-specific solutions. Our expertise extends to various network protocols. We are adept in designing, implementing, and maintaining systems for smart homes, IoT, and industrial automation. We have a proven track record in handling protocols like Z-Wave, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, and Bluetooth 5.0.
Our engineers created a comprehensive system that includes sensors, a cloud platform, a web dashboard, and a mobile app. The signal transmission from the sensor to the cloud is performed by LoRaWAN and Bluetooth 5.0, demonstrating our proficiency in integrating multiple IoT communication protocols. The solution also includes GPS for outdoor parking and Bluetooth 5.0-enabled MCU for indoor positioning, showcasing our ability to adopt IoT technologies for location tracking.
In another project, we engineered a LoRaWAN gateway specifically tailored for IoT/M2M applications. This gateway, designed for communication in large-scale public networks under a single operator, is a testament to our technical prowess in IoT connectivity. The gateway operates by receiving packets from LoRaWAN end nodes and forwarding them to a network server. It is capable of handling messages from thousands of end nodes, demonstrating its scalability. This solution also employs standard IP connections, acting as a transparent bridge that converts RF packets to IP packets and vice versa. This project also underscores our deep understanding of network protocols and our ability to implement them in practical, real-world applications.
For projects involving any network protocol, Sirin Software is the ideal partner. We offer customized solutions that meet your objectives. Contact us to learn how we can help make your project a success.
FAQ
How are these wireless technologies employed in IoT?
Commonly used in IoT devices, these wireless technologies facilitate energy-saving, low-bandwidth, and reliable connections among various smart devices, such as sensors, appliances, and controllers for a range of smart home and automation applications.
What are the distinctions between the two communication systems?
Although both serve to connect smart devices, they exhibit some differences. One can manage more devices simultaneously and deliver faster communication, while the other boasts a superior signal range and reduced connection problems.
Which option is more advantageous?
When comparing Zigbee vs. Z-Wave, the most suitable protocol for your needs depends on your specific requirements and use case. Zigbee may be a better choice for larger networks with numerous devices, while Z-Wave may be more suitable for smaller networks with fewer devices. Zigbee offers customization at the cost of complexity, while Z-Wave emphasizes user-friendliness.
Are Zigbee and Z-Wave compatible with each other?
Zigbee and Z-Wave are not directly compatible, as they operate on different frequencies and utilize different communication protocols. However, some smart home hubs and controllers support both Zigbee and Z-Wave, enabling seamless integration of devices using these protocols within a single smart home ecosystem.
Is it possible to use devices based on both systems in a smart home?
Yes, you can, provided you have a hub or controller that supports both protocols. This allows you to choose devices based on their features, functionality, and compatibility with other devices in your smart home system, regardless of the underlying communication protocol.